Let's get clear, vitamin D is more than a vitamin. And not a true vitamin at all. It's actions are like a hormone, which it is, but first here is what you need to know about this "vitamin" hormone.
- Vitamin D operates in the body in a number of different forms.
- Sunlight acts on cholesterol in the blood near the skin turning it into a pre-vitamin D form.
- The Liver turns this pre-vitamin D form into the storage form mentioned next.
- There is a long term storage form found in the blood as 25-OHD3, the one Doctors measure.
- Both low levels and high levels of this measured storage form of vitamin D can be associated with adverse results. ref ref** <article on same study from Harvard Medical
- CRITICAL POINT: Storage form vitamin D can be found either bound wtih a strong vitamin D binding protein, (VDBP) or in a free or weakly bound abumin form.
- The free form of the storage Vitamin D is associated with bone density while the total that includes the form bound with VDBP is not.
- But, VDBP levels appear to be related to some cancers.
- Both forms need to be measured for proper information to handle conditions. (see below)
- The Kidneys produce an enzyme that converts the storage form into the short lived hormone form, 1,25 (OH)2 D3, when it is needed.
- This hormone form is reponsible for the majority of vitamn D functions.
- The hormone form of vitamin D combines with a form of vitamin A, retinoic X receptor, RXR, before this new compound attaches to Vitamin D Receptors, VDR, on certain cell walls to elicit gene transcription to build proteins that are the carriers of actions attributed to active hormone vitamin D.
- Vitamin D is also available as a supplement in the vegetarian form made from irradiated ergosterol from mushrooms. This form is vitamin D2. The natural sunlight and fish oil forms are vitamin D3. Vitamin D2 is not as long-term effective as D3 and should not be used. A lichen "plant" source of D3 is available.
- The level of free calcium, calcium ions, in the blood is the trigger to start this conversion process.
- The parathyroid gland hormone PTH is the element to carry out this process and it acts until the exact blood calcium ion level is achieved.
- The actions accorded to vitamin D are from the hormone form.
- PTH activates the conversion of the storage form into the 1000 times stronger acting hormone vitamin D form.
- The chief function of the hormone form of Vitamin D is to direct certain actions to help PTH maintain the proper calcium ion blood level.
- This process also helps Vitamin D assist bones by absorbing minerals, but vitamin D also has immune system work in fighting infections and microbes by building LL-37. ref ref
- The storage form does have benefits, but it only exhibits vitamin D actions after it is converted to the hormone form in the blood and also in certain cells and tissues.
- A third form of Vitamin D formed from 25-OHD3 is called 24R,25(OH)2D3.
- 24R,25 (OH)2D3 is a breakdown metabolite of vitamin D and may have opposing (and/or synergistic) effects on 1,25(OH)2D3 in bone building. Quite possibly, 24R,25(OH)2D3 works to mature matrix cells so that the hormone form of Vitamin D can go to work on them. In this way it could act as a control mechanism for hormone vitamin D actions. As part of this control, it may also speed the destruction of and elimination of the active hormone form of vitamin D when it senses job complete, blood calcium level control.
- Both 25-OHD3 and 24R,25(OH)2D3 might need to be known for optimal D level measurements.
- (New) Vitamin D Binding Protein, VDBP ratio to 25-OHD3, is another controlling factor for vitamin D actions by limiting bioavailable of 25-OHD3 for processing and functions (see below). ref
- VDBP is really a mis-named element. It has many other functions which is why taking excess vitamin D could bind up too much VDBP and potentially limit VDBP actions in other areas (although this is rare since VDBP amounts are almost always sufficient). ref
- Vitamin D bound to VDBP is not at that moment available for use by the body, it is storage for a future time. About 85% of plasma vitamin D is bound to VDBP. ref
- Many conversions of vitamin D take place before the final active hormone form is produced. These conversions require magnesium, listed as Mg in circle on this chart
- If magnesium levels are low, (65% are deficient) this would inhibit vitamin D conversion and storage in the blood and give low D readings. ref ref
- Vitamin D genes help direct the building a non-active protein called osteocalcin which has as one of it's primary functions once activated to bind calcium into bone. ref
- Osteocalcin is activated by vitamin K2 to not only perform this building bone function, but osteocalcin also helps regulate blood sugar levels. Maintaining the correct dosage ranges for vitamins D & vitamin K is vital to this blood sugar control mechanism. Still more to discover. ref
- Vitamin D and vitamin K are team members that work together to not only control bone building, but also to regulate blood sugar as well as to limit artery, vein, and soft tissue calcification, plus new information shows it also helps control prostate cell growth. Dr report ***
- Vitamin D by itself might increase artery calcification while together ref, vitamins D & K limit this process and keep calcium going into bones and not into arteries.
- Higher is not always better in older people. ref This reference mentions lower D levels associated with longevity if certain gene mutations are not present. This gene mutation increases D levels and is associated with shorter lifespan. Very interesting! (Since this study is opposite of many others, it has to have other research to support these findings. The gene changes could be responsible and need to be compared to genes in other studies where the opposite results were obtained.)
- NOTE: You will find in studies there are 2 different ways to measure and report vitamin D levels. One ng/ml is equal to about 2.49 nmol/L. This means 20 ng/ml is equal to about 50 nmol/L.
- Vitamin D participates in innate immune system by producing LL-37, a peptide with antimicrobial actions, especially against TB.
- Vitamin D receptor also works with Bile Acids to detox and protect intestinal gut barrier and gut bacterial health, reducing potential for bacterial overgrowth and barrier compromise. IBS?
- Vitamin D is under investigation for LL-37 effects on AIDS progression.
- Vitamin D also decreases beta amyloid production in the brain and speeds breakdown. ref
- It has to be determined if disease lowers vitamin D levels or low vitamin D levels cause disease.
- The active form of D combines with Vitamin D receptors, VDR, and not only regulates PTH levels, but also it's own levels. New research is showing how vitamin D/VDR actions help destroy cancer cells. ref
- Vitamin D has to combine with a from of vitamin A, 9-cis retinoic acid as RXRa or RXRb, before any of the VDR functions happen. ref
- Hormone D actions on tissues chart
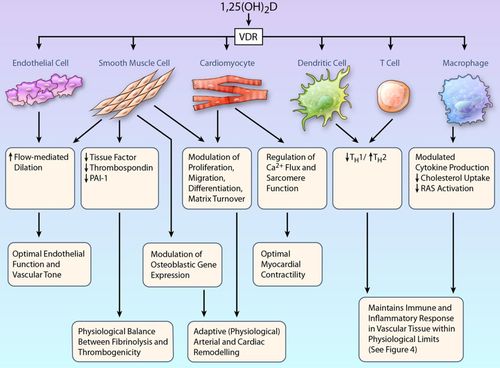
TWO IMPORTANT POINTS OF VITAMIN D FUNCTIONS NEED MENTIONING
- Vitamin D as the Hormone form is generated to maintain calcium and phosphate levels in the blood. When blood levels of calcium get too low, Hormone D is generated to increase calcium absorption from food in the digestive system and stop elimination of calcium out of the body. If that is not enough, the hormone D also can pull calcium out of bones. Calcium is needed in the blood at 1% to help muscles contract, nerves fire, and enzymes react.
- FYI: Nature builds in checks and balances for processes. While vitamin D is pulling out calcium by dissolving bone, it is also telling bone building cells to get ready to re-build more bone to replace what the current necessary activity is breaking down.
- Over the last ten years, another vital function for vitamin D was discovered. This time the vitamin D storage form plays more of a role which surprised Scientists since mostly this form was thought of as being inert without any function. It is needed at levels sufficient to allow it to go into at least 36 different cell types and at least 10 different organs and tissues. INSIDE THESE CELLS AND TISSUES, THE LOW ACTIVE STORAGE FORM IS CONVERTED INTO THE ACTIVE HORMONE Vitamin D FORM WITH THE HELP OF AN ENZYME PRODUCED IN THE KIDNEYS AND LIVER. The Hormone form of vitamin D is 1000 times stronger acting than the storage form. The storage form lasts in the blood for many weeks while the hormone form lasts for only hours.
- This process protects the cells and tissues to prevent DNA damage which could lead to tumor cell promotion as well as insure immune functions to prevent and fight off infections.
- Discussions on Vitamin D dosage need to address both of these functions to arrive at the maximum/minimum and most beneficial vitamin D storage form level.
- As research results are reported, there appears to be certain levels of the storage form for vitamin D that give the optimal action across all activity areas. Not too low, BUT NOT TOO HIGH EITHER. ref
- The mega-dosages available now in stores such as 5,000 and 10,000 should NOT be used for long periods of time, over 2 months, unless under Doctor's care and monitored for blood levels.
- Health articles are full of mis-information, a time for precautionary principles.
- A concept getting reported as if it was fact has a serious flaw. 10,000 IUs is not necessarily safe because that is how much sunlight appears to generate in a short period of time, 20 minutes using a tanning bed. article
DBP - The Vitamin D Binding Protein that is changing the D story
While the function of vitamin D binding protein, DBP, has been observed for a long time, it is only quite recently that a new twist has emerged. It concerns the nature of the strength of these bonds. About 85-90% of 25-OHD3 is strongly bound to DBP while 10-14% is weakly bound to the protein albumin with just 1% of 25-OHD3 as free unbound. This now has new significance as 25OHD-DBP is so tightly bound that it is for all intensive purposes, not bio-available for body functions. It just serves as storage form that can later be unbound from DBP so the Kidneys can convert into the hormone form as needed. ref
FYI: Check out these vital functions attributed to vitamin D binding protein (DBP) ref
Thus, it is only the 10-15% of 25-OHD3 bound to albumin or free form that is bio-active. It is this amount that shows an association with higher bone mineral density while the DBP bound 25OHD3 does not. This bio-active amount can be further modified by genetics about 35%. ref
Of Interest: Mono- and Polyunsaturated fatty acids lower DBP affinity for binding with the 2 vitamin D forms. Saturated fats do not influence. This may have advantages or disadvantages depending upon current body conditions. ref
PLEASE READ THE NEXT 3 ARTICLES ON VITAMIN D FOR SOME INSIGHT AND CLARIFICATION. Article 1. ALL THE ANSWERS ARE NOT YET KNOWN. ref includes questions the US institute of Medicine still needs to clarify for RDI amounts. Here is an interesting work on Vitamin D myths.
FYI: Animal studies show that higher amounts of hormone vitamin D (1,25(OH2)D3) are associated with lower calcification in arteries. ref This is a good thing as artery calcification means artery disease is occurring. Thus, the opposite, lower hormone vitamin D levels, would mean arteries are healthier. This seems to be a paradox since Nutritionists always say to take more vitamin D for strong bones. Remember, supplemental vitamin D is in the storage form and not active. This storage form does not relate directly to the levels of the hormone active form. But, an explanation is needed. Stay tuned!
**This new reference needs to be enhanced. Higher dosages of vitamin D supplements REDUCED bone density over 3 years. At 3 years, the reductions in bone density for the different groups: the 400 IU group down -1.2%, the 4000 IU group was down -2.4%, and the 10,000 IU group was down -3.5%. This is a real eye popper. You do not need high dosages of vitamin D. BUT, there are some potential defects in study methods. The test subjects were mostly at normal levels of vitamin D storage form. This may not repesent the larger population where deficiency levels are more pronounced.
***This Doctor report is included for the information on actions of Vitamins D and K2, NOT for the recommendations of amounts. Since this Doctor was using his patients, the patients were being tested and medically monitored. Thus, he could adjust dosages based upon test results. There could be other associations that might influence different conditions under D and K2 control such as blood sugar maintenance that were missed by this Doctor looking only at the one condition in question, or the conditions that may only reveal over time, plus the aspect of individual variations.
Many different disease conditons have vitamin D associations, such as artery and heart health, bone strength, blood sugar regulation, and also a number of cancers. It looks like there many also be different dosages of vitamin D optimal for each conditon. This appears to present a problem for determing the ideal vitamin D supplement dose. Going overboard is not the asnwer, especially for bones. article What is the ideal amount? article