While Omega 3 fats have almost reached legendary supplement status as fish oils EPA and DHA, the truth is the body needs only the following two essential fatty acids;
1. Linoleic acid (LA), an omega 6 fatty acid
2. Alpha Linolenic Acid (ALA). an omega 3 fatty acid
The Omega 3 fatty acids EPA and DHA from fish and algae are often mentioned here and since the body can build them from ALA, they are not considered essential. BUT, some, perhaps many, people have difficulty converting ALA into enough EPA and DHA, some fish or algae source is probably wise. Fish get or gain omega 3 fats by eating algae, krill, or smaller fish. 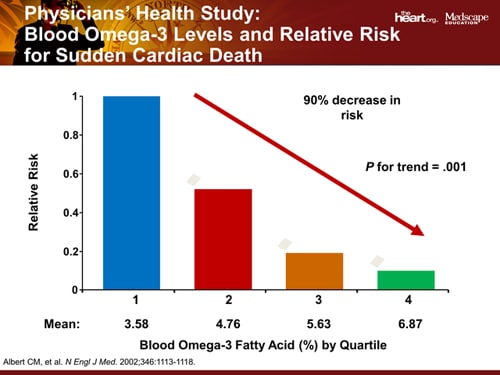
Modern dietary food choices and processing methods have changed over the last century that dramatically reduced omega 3 fatty acid consumption while increasing omega 6 from vegetable oils. Wise Nutritionists often talk about a ratio or balance needed between omega 6 and 3 since the reduction in omega 3 can play a major role on declining health. Perhaps the largest decrease in omega 3 came about as cattle left the grass pastures and entered corn grain feedlots. This reduced omega 3 and increased omega 6 in beef fat by a factor over 3, from a ratio of 1 to 4 down to 1 to 15. The bacteria in the cow changes with grain feeding and this bacteria produces less omega 3 in beef.
Of a cautious note: A new study suggests that women should not use high dosages of Omega 3. It may upset fatty acid balance. Therefore, the goal is to find the most efficient omega 3 format that gives greater benefits than taking a higher amounts of lower quantity omega 3. Krill oil fills this bill. The little Krill are a vital food chain link for many Ocean Fish. Krill oils contain some phospholipids instead of only fatty acids in the triglyceride make up that may give them extra benefits over regular fish oils. ref
Omega 3 oils contain different degrees of EPA and DHA structured fatty acids. As fish oils are concentrated during processing, their structure changes. Omega 3 fatty acids are needed for both energy production and cell membrane integrity. Membranes surround cells to protect cells and allow nutrients to be transported into and waste products out of cells. Nerve cells in the brain contain large amounts of DHA. While all fish oils supply omega 3 for energy, the ability to build healthy brain cell membranes is sometimes low to begin with or altered during processing. This is where Krill show greater effectiveness over other fish sources and processing methods.
CAUTIONARY NOTE: Fish oils and other unsaturated fatty acid oils are very large molecules making them extremely perishable. ref These large fat molecules are susceptible to the process of lipid (fat) peroxidation. They should be refrigerated to prevent rancidity from this process as well as they need to be protected in the body with some extra antioidants, like Vitamin E or CoQ10. Buy bottles of smaller softgel numbers and handle appropriately. High fish oil dosages should be monitored by a Doctor. While the native people of Alaska have little heart disease due to abundant omega 3 oils, they do suffer more strokes from the effect of omega 3 thinning blood. ref
OMEGA 3 TO 6 BALANCE
There is now a lot of research on omega 3 fish oils and their beneficial effects on cardiovascular disease. Omega 3 helps reduce inflammation that is generally increased by too much omega 6 from vegetable oils. So, there is a tendency to call omega 3 fats "good" and omega 6 fats "bad" which is unfortunately, an incorrect picture. Both omega 3 and omega 6 are essential for health. ref ref
But, there is a balance between the two that should be respected. ref Plus, there are good omega 6 sources and some not so good ones, like in French Fries. Prepared foods often have altered fats called trans-fats, listed as partially hydrogenated oil. Beef and eggs in the old days contained a lot of omega 3 fat but not so today.
The good omega 6 fats are as responsible as omega 3 for controlling inflammation. One omega 6 in particular, arachidonic acid, is thought to be the bad guy and, yes, it is directly involved in producing pro-inflammatory elements. But, as nature often does with bad guys, there is a positive role that arachidonic acid plays as well.
One way, Arachidonic acid helps regulate neuronal activity. To control the bad guy image, nature uses the level of omega 3 EPA to balance out the good and bad in Arachidonic acid. Thus, this is the reason a balanced ratio is needed between omega 6 and 3 lower than 6:1, with 4:1 looking ideal. In the diet today, it can often be over 20:1. It may be that just a certain amount of omega 3 is needed to control the cascade of omega 6 into pro-inflammatory elements and the exact ratios are less critical. Or that a reduction in the bad types of omega 6 will also help without achieving an exact ratio, as well. ref ref