The Calcium Paradox**
 Saturday, May 15, 2010 at 11:25AM
Saturday, May 15, 2010 at 11:25AM For a Lifetime of Strong Bones
UPDATE: To benefit immediately from new research, limit calcium supplementation to no more than 600 milligrams unless you know your dietary intake amount. The safest total amount with diet and supplement sources added together falls between 600 mg to 1000 mg per day. Dietary daily calcium load is usually between 300 to 800 milligrams. Many foods are fortified with extra calcium, like orange juice and cereals, so supplemental calcium at 600mg may actually be a little high for some. To be fair, here is another study around the same time that arrived at what appears to be an opposite heading, that higher calcium is protective. BUT, look at the dosages for the higher and the truth is revealed (lower <458 mg/d for men, <417 mg/d for women versus the higher quartile of dietary calcium intake (>762 mg/d for men, >688 mg/d for women). ref Here is another study showing longer term benefits against osteoporosis but not for 3 year fracture prevention. ref (Note that the long term benefits were assumed and not a verified fact using just the measurement of increased bone density at 3 years.)
FYI: Women tend to benfit more from increased calcium and vitamin D than men. Men should limit total calcium from diet and supplements to under 1000 mg per day. ref
...YOU HAVE TO KNOW HOW MUCH DIETARY CALCIUM YOU CONSUME DAILY BEFORE YOU ADD CALCIUM SUPPLEMENTS.
1000-1200 mg minus dietary or food calcium intake determines how much or if you should supplement. ref If daily calcium intake is low, supplements may be necessary. BUT, if consumption is already high, little if any extra calcium supplementation is needed. The concept of supplement calcium load spike is involved here. Therefore, it is wise to take any supplemental calcium in small divided dosages. And include adequate vitamin D and vitamin K2, with MK7 preferred over MK4 or K1, as well as the other synergistic minerals, such as phosphorous, magnesium, zinc, and potassium. Elimination of calcium in urine is appropriate to measure, but it varies with many different factors. It is a guide not a steady data point. Dietary calcium intake influences amounts and they vary from about 20-250 mg. with over 250 representing excess calcium elimination. Highest ever recorded was 741 mg. but that is rare. The urinary calcium level can be used to determine bone turnover rate. It is often elevated in osteoporosis and renal stone situations. ref ref
From the Harvard Medical School newsletter:
Calcium helps make strong bones, and vitamin D aids calcium absorption. Take a daily vitamin D3 supplement (D3 is the form most easily absorbed) between 600 to 1,000 IU, depending on your blood levels of vitamin D. For calcium, some evidence indicates that large doses of calcium pills may increase the risk of death from heart disease. (ref) So as much as possible, get calcium from food—dairy products*, leafy dark green vegetables, tofu, and sardines. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of calcium for men ages 51 or older is 1,000 to 1,200 milligrams (mg) per day. For women ages 51 or older, it's 1,200 mg per day. ****If your diet doesn't provide enough calcium, take a low-dose calcium supplement to reach your RDA, but not exceed it.**** ref
*Dairy products do not contain enough magnesium to balance calcium in body. Be sure to supplement with some magnesium or add foods rich in magnesium.
REMEMBER: Add up food calcium amount together with supplement amount to not go over the recommended amounts at 1,000 or 1,200 milligrams total per day. DO NOT SUPPLEMENT 1000 MG. ref The diet has between 300-700 mg. One serving of dairy has 300 mg. of calcium. Plus, it may not be appropriate for some people to consume these high levels of calcium without knowing amounts of other related nutrients.
Somehow, over a period of time, simple logic (and Science) lost out to marketing rhetoric in telling the bone health calcium story. At fault, science is not even following it's own scientific protocols in examining theories for credibility. The Calcium dance may be one of the most complex nutritional issues of our time. More is not always better. ref cautions> ref Excellent general Calcium info from Harvard Medical> ref Bone info, ref
Calcium is vital to health
 What you think are calcium facts are really marketing stories not entirely based on science, or at least not the whole picture but just small segments. Unless you have an understanding of the principles involved and correctly apply them, you are doomed to suffer mis-steps in the CALCIUM dance. Bones are just the tip of the iceberg for calcium actions, and while difficult to believe, calcium is not even among the top few recommendations from science for healthy strong bones. ref ref
What you think are calcium facts are really marketing stories not entirely based on science, or at least not the whole picture but just small segments. Unless you have an understanding of the principles involved and correctly apply them, you are doomed to suffer mis-steps in the CALCIUM dance. Bones are just the tip of the iceberg for calcium actions, and while difficult to believe, calcium is not even among the top few recommendations from science for healthy strong bones. ref ref
Here is a key bone basic from the US Surgeon General's report ref : "The bony skeleton is a remarkable organ that serves both a structural function, providing mobility, support, and protection for the body, and a reservoir function, as the storehouse for essential minerals."
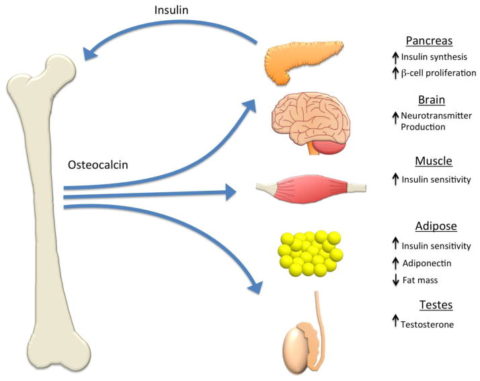
Absent from this report is the fact that fats and bones interact and serve an endocrine function for energy metabolism and insulin resistance. article ref.
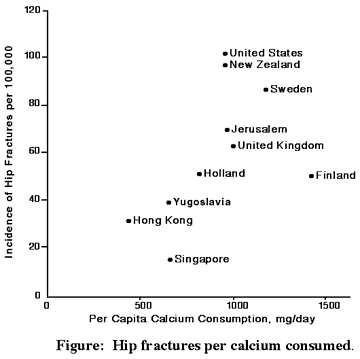
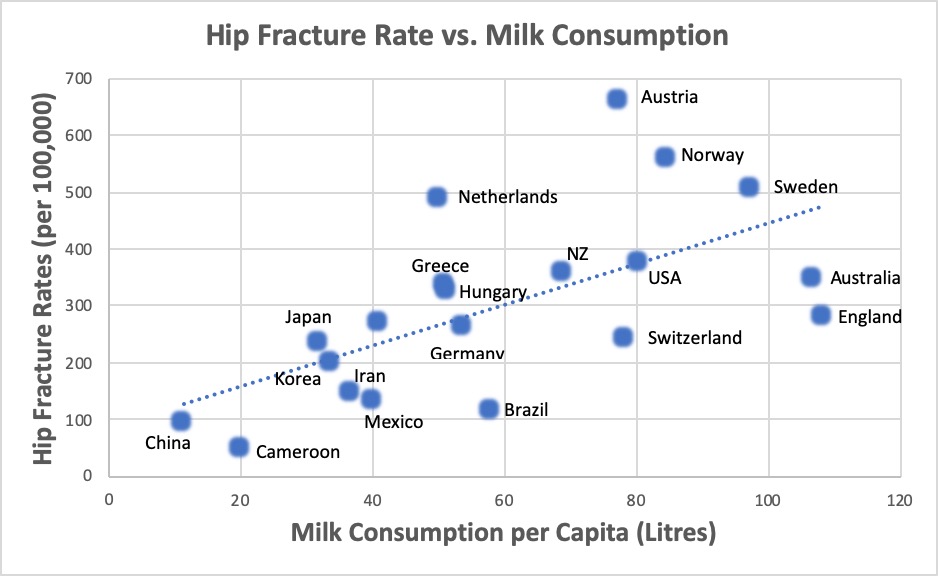
Here are study results mentioned above for milk drinkers exhibiting more hip fractures when 3 or more glasses consumed per day. Three glasses of milk could supply over 900 mg of calcium. But not nearly enough magnesium. Questions about study are also mentioned. Direction but not absolutes.
Next reference below is a report from Italy, thus might not be completely USA similar, that shows supplemental calcium load has to be added to dietary amounts to get to 1000 - 1200 mg per day.
Click here>J Int Med Res. 1999 Jan-Feb;27(1):1-14.
The Calcium Paradox**
**VITAL ANALYSIS LINKS ABSENT FROM BONE HEALTH DISCUSSIONS**
Calcium has many vital roles to perform in the body to maintain health, and not just for bone density. Calcium supplements and calcium fortified foods have become major players in dietary programs recommended by Doctors and Nutritionists. Many foods are now calcium fortified. The theory goes like this. Bones are made up of collagen protein structures that form a matrix of inner-connecting tubes, very similar to honeycomb in a beehive. Next, minerals fill in the spaces left in theses tubes to give more strength. Since calcium is the most abundant mineral found in bones, it was assumed that taking more calcium would increase bone mineral density and thus prevent future fractures. 
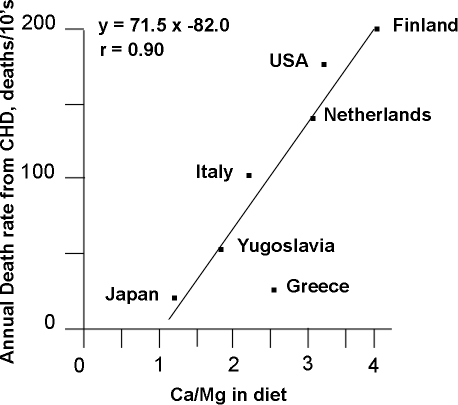
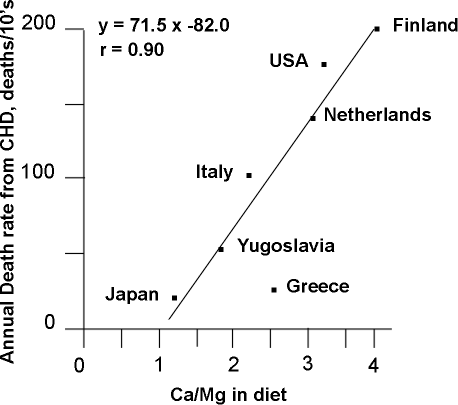
A logical look now at the facts reveals this assumption might not be entirely true. ref (controversial) Countries with the highest dietary intake of calcium often have much higher bone fracture rates than countries where the people consume less than half as much calcium. In studies of healthy young people, adding extra calcium does increase bone density, but when the studies end and the extra calcium is stopped, the density levels return to the pre-study level. Vital Fact # 1 is that bones act as a calcium storage area. Yes, it is not always a fair comparison since in lower calcium consuming Countries there is increased exercise, and possibly higher sun produced vitamin D. Muscle movement is a major factor in generating stronger bones.
MAJOR CALCIUM FUNCTION
Let's for the sake of discussion, assume that bones indeed act as storage for extra calcium. What purpose for the body would this calcium storage function serve? The body has a very elaborate mechanism to regulate calcium levels. This allows the body to adapt to a wide range of calcium intake levels and still maintain healthy calcium functions such as strong bones. But there are limits. The driver of this process is not the amount of calcium in bones, but the level of calcium in the blood. A one percent calcium amount is needed in blood to allow nerves to fire, muscles to contract, enzymes to work, and for cells to die a natural death at the end of their lifespan.
When calcium blood levels dip a little too low, the parathyroid gland secretes the hormone PTH which activates the production of the hormone form of vitamin D to regulate the following functions; It increases calcium intake from food during digestion, it prevents calcium elimination from the kidneys and colon, and if needed, it takes calcium (and thus also magnesium, a little zinc, and phosphorus) out of bone storage.
When blood calcium levels become a little too high, the thyroid gland secretes the hormone calcitonin which shuts down PTH production that turns off the activation of the vitamin D hormone form. ref* This reduces the intake of calcium from the digestive tract and increases elimination out of the kidneys and colon. Plus it stops pulling calcium out of bones and starts to increase bone densities. This action could also be a residual effect of PTH and the hormone form of vitamin D to stimulate the production of bone building as well.
FAILURE OF HIGH CALCIUM INTAKE
If you take high amounts of supplemental calcium everyday, while the body attempts to compensate, the results may not be advantageous for either the health of the body or long term fracture prevention. ref ref ref (risk and benefits)
Let's follow the logic:
- High calcium from food rarely reaches detrimental effects since dosages are low plus buffers also present in food to further limit absorption. Thus it is supplemental calcium that tends to become problematic, or from supplement and food sources added together.
- First, high calcium intake will increase blood levels and stimulate calcitonin production which shuts down calcium absorption from the digestive system by turning off hormone vitamin D activation.
- The Kidneys start to increase calcium elimination and decrease colon calcium percentage absorption.
- Plus, the extra calcium that gets into the blood will be sent to the bones for storage.
- Bone building cells are activated to make this happen. They can pack more calcium into already built bone cells, plus also into the new bone cells constantly being built. (osteocytes, ref)
- Normally, these actions would sooner or later result in a balanced calcium blood level with future days swinging slightly back and forth when high or low calcium intake triggers opposite processes.
- But, taking large doses of calcium supplements (and calcium fortified foods) everyday changes this pattern to always be on the high side, even though the body is ramping up it's calcium anti-absorption and faster elimination processes. Calcium levels may still increase due to osmotic gradiant competitive absorption of minerals in the lower small intestines.
- ***Supplements release calcium rapidly into the system and this spikes blood levels. In contrast, food source calcium, usually at much smaller dosage amounts, releases gradually allowing for smaller spikes in blood calcium levels at one time. These lower amounts help the body properly deal with calcium and other minerals without over stimulating body control and regulation influences. Food sources also contain many nutrients with buffering effects to further control mineral balance.
- To understand the implications of this higher blood calcium level pattern, you need to know about mineral absorption channels as well.
- UPDATE: Higher calcium supplement intakes are associated with deceasing storage form of vitamin D levels in blood stream of subjects not deficient in vitamin D, without vitamin D supplements having any impact. ref
- There could be a negative vitamin D response to higher calcium supplement intake. This does not change with vitamin D taken at the same time.
- In subjects who are low in vitamin D, the result of calcium and vitamin D normalizes vitamin D levels in females.
CAUTION SENIORS: It has to be mentioned that certain forms of calcium are more difficult to absorb than others. Check out this study. Calcium carbonate is difficult to absorb for older folks and can cause problems, especially since it lowers stomach acid. But, the differences are not as large as expected. Follow the recommendations in the previous linked study as Protein digestion could become a related problem. The new plant source calcium in red algae is present as calcium carbonate, even though this is not mentioned on the label. Of note is that the calcium carbonate in limestone is all in the form called calcite. The red algae plant adds two extra forms, aragonite and vaterite with calcite. Vaterite has greater biogenerating and reacting abilities, thus is relatively unstable and present in small amounts. Aragonite can break down to calciite. These different forms give red algae calcium carbonate only about a 10-15% absorption and activity advantage over limestone calcium carbonate, plus the benefit of a small amount of other minerals.
Caution Senior 2: It has been discovered that some Seniors have limits to the conversion of the storage from of vitamin D into the hormone in the Kidneys. Something blocks an enzyme needed for this conversion. ref This lowers the action of hormone D to increase calcium absorption. Calcium balance goes negative leading to bone loss. This may be one reason some Nutritionists recommend much higher intake amounts for Seniors. ref Above a certain level, passive absorption can be forced. This unfortunately could also lead to calcium ending up in the wrong areas.
MINERAL ABSORPTION PRINCIPLES
- Calcium is one of just a few minerals to have an active absorption process in the first third of the small intestine. Elements (from hormone vitamin D) are secreted into the intestinal track, combine with free floating isolated calcium, and carry it back into the cells lining the intestinal tract for assimilation.
- The other minerals are mostly absorbed in the next two-thirds of the small intestines by simple osmotic gradients depending upon their concentration to each other. This point is critical.
- After the body actively pulls in the amount of calcium it wants directed by body needs (rarely more than about 200 mg. at each meal), any calcium left in the intestinal track participates more or less in a free for all to gain access through osmotic gradient channels competing against all the other minerals.
- Since calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, and zinc all compete, excess levels of one could reduce the amount of the others that get absorbed. ref ref
- ***Magnesium is needed to maintain and control calcium levels inside cells.*** ref ref
- Mineral ratios to calcium impact body processes beyond the level of the body's ability to compensate for some imbalances. Calcium over a 2:1 ratio with magnesium is counter productive to health. Most foods average a 1:1 ratio when dairy is not considered.
- With just food levels of these minerals, this competition does not reach the degree it can with higher supplement amounts. Plus, the over consumption of just one food group, dairy, might also create changes to mineral absorption rates and balance since dairy has a calcium to magnesium ratio of 10 to 1.
- If this was not enough to have to consider, along comes some food types with mineral binders, such as the phytate content of beans, especially soy. Almost all the minerals in soy are bound up by phytates in the small intestines and eliminated out of the body. Fermenting soy de-actives much of this phytate action.
- STRONTIUM <everything you need to know and more. Here the important fact is that strontium competes against calcium for absorption. If you unwisely consume strontium, it is recommended to take calcium at a different time. CAUTION: Do not take high doses of strontium over 100 mg unless you are under a Doctor's care. After 10 years, research now shows there is a greater cardiovascular disease risk.
Here is the rub from continual high intakes of calcium; it turns off the production of the active hormone form of vitamin D. This lowers the amount of calcium absorbed by the active process. Which of course makes more calcium available to participate in the mineral free-for-all for osmotic absorption in the rest of the intestines against all the other minerals. High chronic calcium intake inhibits the absorption of many other minerals, such as magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc. Does this sound like a good idea?
Insight: THE BODY IS NOT DESIGNED TO HANDLE LARGE AMOUNTS OF CONCENTRATED SUPPLEMENTAL CALCIUM, or any other mineral. Nature limits mineral levels in food and often includes buffer elements to further slow down and regulate absorption. In foods such as dairy where one finds high levels of calcium, nature never intended this food to be consumed for a lifetime. The infant needs these larger amounts (a relative term) of calcium to turn soft cartilage like bones into hard solid bones able to support upright walking and increased weight gain.
When you read about the benefits of vitamin D, they are mostly from the active hormone form and not the passive storage form generated by sunshine and supplements. The passive form serves as the material for the Kidneys to make the active hormone vitamin D. Yes, there is another important function for the passive D form. At the proper levels, it goes directly into certain tissues such as breast, prostate, and colon where it produces the hormone D form locally to protect these tissues. This is why it needs to be kept at an optimal level, not too much or too little.
NOTE: Some Nutritionists say Vitamin D levels are too low and recommend larger doses. They point to studies that do not find a benefit as testing too low a vitamin D dose. Check out this study that measured vitamin D levels both as inert 25-OHD and the hormone form 1,25OH2D in children with Rickets. Vitamin D levels did NOT show profound differences, with even higher hormone form activity in rickets, but still no increase in calcium absorption. Many questions left unanswered. Here is another study that shows extra vitamin D in healthy younger women does not increase overall calcium absorption. Then this study comes out that higher intakes of supplemented vitamin D actually result in greater loss of bone mineral density. The levels of vitamin D tested were between 400 IU, 4,000IU, and 10,000 IU in 360 subjects for 3 years, The 400IU group lost the least density over this period. Some calcium was also included at 600 mg.
USE OF BONE HORMONES to PREVENT BONE LOSS
While research is not conclusive on this, it is interesting that the only hormone treatment showing promise to aid bone health, out of attempts using the three natural hormones involved in blood calcium balance, is the intermittent use of PTH. To accomplish this naturally requires the diet to vary between higher and lower calcium intake days or periods of time. Remember low blood calcium levels are the trigger for PTH production while high blood calcium levels turn it off. Science found that continual use at constant amounts of either PTH, calcitonin or calcitriol (hormone vitamin D3 form) all exhibited adverse effects. This might mean you should not take calcium supplements every day, or at least not always at the same amount, in an attempt to get PTH levels swinging up and down to mimic the only condition science found effective for long term bone health. This aspect makes sense, but have you ever heard nutritionists and dietitians mention this factor? Or researchers study and test this theory?
BONE BUILDING CELLS - LIFESPAN FACTOR (**NEW**)
Long term studies are not showing the expected prevention of bone fractures from high intakes of calcium or dairy. It is time to acknowledge another potential concept recently discovered. Bone cells have a controlled lifespan due to the replicative capacity theory for most cell types. Bone cells divide a set number of times before they die a normal death. A lifetime of high calcium intake which demands that the body pack extra calcium in bone cells or build new ones more frequently, may in fact wear out the bone building cells too soon. Or simply not enough of them are produced. ref Osteoporosis would develop and there would be less options to mitigate condition at this point, but at least it would indicate the appropriate treatment protocol. This process is known as cellular replicative capacity. Inside bone, osteoblasts turn into osteocyctes which continue to repair bone tissues. These cells do not divide and live 25 years, but are prone to damages and destruction if overworked. ref
An analysis of the age of bone building cells from people with osteoporosis reveals that more of these cells are indeed at a later stage of their natural lifespan compared to those in people without osteoporosis. Older bone building cells simply do not function at the level the body requires to balance with the still robust activity of bone tearing down cells. These two actions are usually nearly balanced in the natural bone repairing program. Unfortunately, the bone tearing down cells evidently do not age at the same rate. This topic will be expanded in future articles since research is still at such an early stage of discovery.
SIDEBAR: It of interest to note that the method of action of many bone saving Drugs is to target the bone tearing down cells by poisoning them so the tearing down activity will slow down to be closer to the limited bone building activity. But, this is a delicate balance to achieve and a few people taking bone drugs have developed major problems such as jaw bone disintegration, perhaps due to an unbalanced bone remodeling process that leaves too much old and weak bones to support integrity of jaw bones. They simply disintegrate from not enough bone building to refill all the holes and micro-cracks in bone.
Where is the pure science and scientific protocols regarding calcium intake and functions? For more details see Boneworks article. ref Dr Mercola has good study resources listed here. Not all study references report the same findings.
VITAL UPDATE: The body has a bone repair process that exhibits a major impact on healthy bones. There are two critical types of bone remodelling cells that are responsible for maintaining strong bones. Small sections of bone are continuously being torn down and new bone is re-built in the space. This is how the body re-news bone and keeps it strong and pliable. The process that controls the activation of these bone repair cells is the RANK, RANKL, and OPG system. article While estrogen helps control and balance this process for many years, it appears after menopause, the system is easily corrupted and generates too many tear down cells and not enough build back up cells. Over time, this generates big holes in bones resulting in weak bones and a condition called Osteoporosis. It may very well be that actions before this time are needed to maintain strong enough bone to last the rest of life. And no amount of bone nutrients or drugs will completely fix this situation, they will only modify to various degrees. Strong bones require a lifetime program.
SIDEBAR: You might have been told to take calcium between meals or at night. If you want to help prevent kidney stones, calcium should be taken with meals so the calcium will bind with the kidney stone generating oxalates found in certain foods and eliminate them out with feces. Many forms of calcium also need stomach acid present at mealtime to help absorption.
A New twist for Seniors on Bone Turnover Rate
For Seniors with osteoporosis, the bone turnover rate is too high. Plus, the remodeling balance of teardown is alot higher than build up so there is a net loss of bone tissue. The bone tissue that is lost is sending the calcium it contained, first into the blood stream, and then out with urine. STOP! What is the effect of this bone released calcium on the bone rebuilding process when it hits the blood stream?
Nutritionist want Seniors to take more calcium, a lot more, up to 1200 mg. When the body gets too much calcium in the blood, it shuts down PTH production which reduces calcium absorption and increases urine elimination. Something is not right with this picture. In the average size person, at a bone loss of 7% per year, this would dump about 230 mg. of calcium per day into the blood stream.
PTH is produced when calcium starts to lower in the blood. This activates vitamin D which helps absorb calcium from the digestive tract as well as stimulate bone building cells. None of this happens when calcium is constantly entering the blood stream in higher amounts. Active vitamin D is needed for other activities like building immune system protection against invading germs.
New Finding on Calcium absoption in Seniors: Scientists have discovered that some Seniors develop a resistance to both the actions of the hormone form of vitamin D to increase cacium absorption as well as the to the conversion of the storage form of vitamin D in the Kidneys into the hormone form. ref
Scientists have found that the way the body functions best for bone building is to swing back and forth between PTH production and shut off. A diet of various calcium intake levels would assist this process. New bone research is forthcoming that will explain the processes involved to a greater degree. There are many factors to consider. One of the chief ones is determined by bone cells called osteocytes imbedded far into bone. These cells appear to regulate the remodeling process through the balance of RANKL activity and OPG production. When OPG decreases and RANKL activity increases, bone is lost. ref
This requires a completely new paradigm in thinking. Return soon for that information. And read this other article on this website.