Vitamin D and Mortality
 Friday, May 11, 2018 at 4:23AM
Friday, May 11, 2018 at 4:23AM Thousands of research studies have cropped up on Vitamin D over the last 10 years. Many looked to see if vitamin D levels impact mortality rates. Here is one meta-analysis, analyzes many already existing studies, that found some vital trends that are quite revealing. Here is the study.
What they found in a nutshell is this: "In conclusion, our results implicated that long-term supplementation of vitamin D may have a beneficial effect on overall mortality, especially in patients with vitamin D insufficiency and younger than 80 years. Vitamin D in a dose of 800 IU daily or less was found to be more favorable than a dose greater than 800 IU and treatment with cholecalciferol (D3) was more favorable than ergocalciferol (D2)."
"Dose of 800 IU daily or less...most favorable"
Here is the conclusion mentioned in the abstract: "The data suggest that supplementation of vitamin D is effective in preventing overall mortality in a long-term treatment, whereas it is not significantly effective in a treatment duration shorter than 3 years. Future studies are needed to identify the efficacy of vitamin D on specific mortality, such as cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality in a long-term treatment duration."
Question: Now, what do you think the upper recommended amount of vitamin D is in the new vitamin criteria presented on this website?
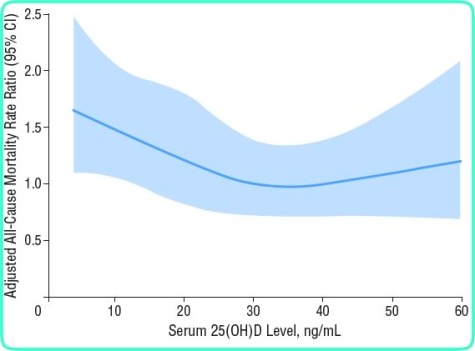
If vitamin D levels were low at the beginning of the studies, less than 20 ng/mL, there was greater benefit from vitamin D supplements than if beginning levels were over 20ng/mL. Calcium with vitamin D was better than vitamin D alone. For bone health, from other studies, a vitamin D reading of over 18 ng/mL appears to be significant enough to protect bones and any increase over this amount had little extra value. But this meta-analysis was looking at overall mortality. Remember this is just looking at associations, and not causes. There are many diseases that have been found to have mechanisms that lower vitamin D levels, like cancer, and this possibly influences studies like this one.
But, there are possible explanations for these results. And this chart seems to uphold this study too. Taking 800IU would likely increase an 18 ng/mL reading up to 26ng/mL after 3 months and with a little sun, a reading of 30-33 would be likely. This appears to be about the same results as shown in the above linked chart. The lowest mortality level appears to be between 25-40 ng/mL. Over 50ng/mL there is a rapid increase in mortality the same as under 20 ng/mL.
QUESTION: Why is the Vitamin D Council recommending very high levels such as 50ng/mL and higher? article This appears to be too high according to the above chart. Still controversy for correct levels to maintain all the different applications of vitamin D involvement. Remember, while low dosages of vitamin D supplements( 800IU) tended to prevent falls in Seniors, higher vitamin D intakes increased probability of falls and thus fractures. ref Fractures of hips in Seniors tend to increase mortality. Is the Vitamin D Council working one factor against another, benefits in one area against detriments in another?
Here is one rational for apparent opposite effects, beneficial if levels low and detrimental if already high. Vitamin D hormone actions include increasing the absorption of calcium from food to maintain blood calcium levels at a vital percent. A problem occurs with higher vitamin D intake, along with the calcium comes many other essential minerals as well (magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, zinc) plus a few undesirable ones too, like lead.
The amount of lead absorbed would depend upon two things, the amount of lead in the foods, plus the amount of the other essential minerals. The proper amount of essential minerals act to block out the heavy toxic minerals like lead. Children are more susceptible to lead absorption. Be careful picking concentrated health foods like vegetable juices, green powders, or rice proteins. All have found lead amounts, as has some plant source calcum from algae.
Unfortunately, the level of deficiencies for many essential minerals is far to high for magnesium (64%) and calcium (49%). These are presenting an open door for lead and other toxic minerals to enter. The detrimental findings for higher vitmain D levels might be due to these toxic minerals and not just to vitmain D by itself. Although there are many ways for the vitamin D system to fail. The number of players involved is far more than almost any other vitamin function.
The players; Sunshine, UV radiation, Cholesterol, 7-Dehyrocholesterol, CYP2R1, calcidiol, cholecalciferol, ergocalciferol, 25(OH)D3, Magnesium, PTH, calcitriol, 1,25(OH)2D3, VDBP, albumin bound D, , unbound D, VDR, VDR/RXR, vitamin K2, ostocalcin, LL-37, vitamin D 25-hydorxylase, CYP2R1, vitamin D metabolites, sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1), calcifediol, 24,25-Dihydroxycholeciferol, P450cc24, etc. Check out chart for yourself.