Candidates for Prostate Cancer (PC)
 Saturday, March 20, 2010 at 9:37AM
Saturday, March 20, 2010 at 9:37AM There are a few associations that warrant further investigation right away.
- Does supplemental Chondroitin influence prostate cancer spreading?
Prostate research has uncovered that higher chondroitin levels around the prostate gland increase the production of a particular protein called versican. This proten attaches to prostate cancer cells and may speed up their spread into other areas of the body. More aggressive prostate cancers are associated with a greater concentration of versican. ref But, chondroitin can also increase another protein called decorin which serves to lower prostate cancer spreading. What influences which one is dominate is still unknown? Or, if there is some way to lower versican and raise decorin.
The question at hand is does taking supplemental chondroitin contribute to body levels of versican around the prostate or is chondroitin destroyed in the digestive process since it is such a large molecule? And thus only chondroitin made in the body influences the prostate? While this issue is still under investigation, the precautionary principle is in play and only glucosamine should be used for joint health. But even glucosamine has some issues in certain situations. article
NOTE: Hyaluronic Acid (HA) also exhibits this potential prostate tumor promotion aspect, or it's suppression, depending upon which one of HA processing enzymes is dominate. ref The molecular size of the HA molecule might also be a factor, with larger generally protective while smaller often detrimental. (to help absorption, vitamin companies break up the larger HA molecules into smaller ones) This is potentially serious as Nutritionists are promoting HA as a fountain of youth. article Note breast cancer link in last reference. ref ref ref ref
- Does a higher Alpha Linolenic Acid intake contribute to Prostate Cancer?
An older study out of Romania revealed that men with higher intakes of Alpha Linolenic Acid, a fat found in flaxseeds, meats, dairy, plus canola, soy, and walnut oils, had increased rates of prostate cancers. This study found most of the ALA was from meat. It is possible that something else in the meat was also a contribuing influence, or maybe even the main factor.
Alpha linolenic acid is an omega 3 fat. Some ALA converts in the body into the same Omega 3 fats as found in fish oil, EPA and DHA. Since omega 3 fats help reduce inflammation and disease, this association was a somewhat shocking discovery. ref updated study
FYI: There appears to be two types of prostate cancer. The more regular slow growing one that men can live with for many years, or the rare aggressive fast growing one with a higher mortality rate. These two types may have different initiating conditions.
Over the 2 decades following the Romanian study, other research looking into ALA and prostrate risk did not always arrive at the same conclusion. A recent meta analysis looking at 16 studies, found only 6 with a weak link for increased prostate risk, and mostly with the more advanced aggressive form. These studies all measured the amounts of ALA in blood or tissues rather that the intake amount of the diet. ref ref ref ref ref
CAUTION: Research has discovered a link between higher alpha linolenic acid intakes and the eye condition macular degeneration in both men and women. ref
Many people take Flaxseed oil as a source of Omega 3 fats. Until more research settles these issues, the prudent approach if you have a family history of prostate cancer or eye conditions might be to limit flaxseed oil to just a couple of times a week and use more of the whole seeds ground up instead. The macular degeneration link may put a damper on flax oil sales as this condition shows increasing numbers.
- What about Lycopene from tomatoes?
In an animal study, Researchers tested tomato paste, tomato powder, or tomato paste (lycopene source) with a concentrated ingredient from tomatoes, a ketosamine, FruHis. Only the last group, paste with FruHis, showed major protection against prostate cancer cell tumors. The other groups did not exhibit fewer tumors or live as long. Gained from other studies, Lycopene by itself does not work, it needs to interact with the ketosamine, FruHis. ref To get enough lycopene and ketosamines for this protection only from tomato products requires very large portions. Remember, animal study results are not always the same as in human studies, but...
- Higher levels of free calcium in blood are associated with increased prostate cancer deaths.
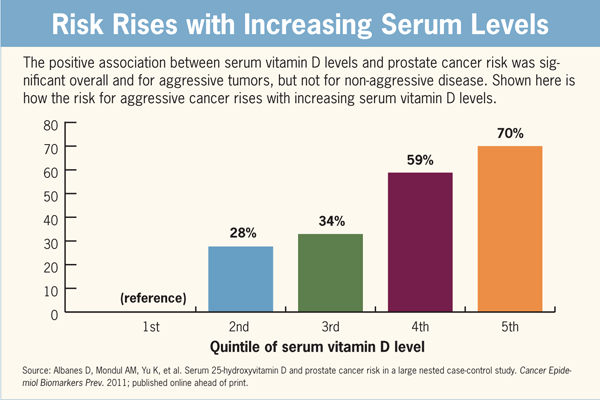
Vitamin D is being recommended for many cancers including prostate. And indeed it appears higher amounts of the storage form of vitamin D as 25(0H)D3 are needed to protect prostate tissue since they develop the hormone D form right in the prostate cells. ref ref
A new study looking at the level of free calcium circulating in the blood compared to calcium bound with protein and total calcium found an association of greater risks for advanced prostate cancers and deaths at higher free calcium levels. Here is a study showing higher pH blood levels (alkaline) lowers free calcium. ref Vitamin D binding protein levels also impact prostate cancer. ref 
While kidney disease influences the free calcium levels, greater vitamin D intake can be associated with higher amounts of free calcium too. This needs scientific research to quickly verify how this plays out.
SIDEBAR: Since the research on Vitamin D levels as 25 OHD storage form of D or 1,25 hormone action form of D are not conclusive for prostate cancer connections, maybe just the effect of D on free calcium (ionized) circulating levels is the marker of value, and not overall calcium or D levels. To lower free calcium, an alkaline pH is needed. This would indicate an acid forming diet may be the real culprit and not just calcium intake and vitamin D levels. ref ref -another form of first ref
NOTE: There is a new theory in the works that says calcium and vitamin D often get the blame when it is really low magnesium and an unbalanced calcium to magnesium ratio that is the real guilty party.
- Excess Folic Acid may increase some cancers such as colon and prostate.
This is really no longer in question. The statistics are pretty convincing. DIETARY folate at certain levels does offer prevention or protection against DNA mutations before cells have turned cancerous. BUT, the next references show a slightly elevated risk from higher blood levels over time. ref Supplements of folic acid doubled the prostate cancer risk in one study. Plus, after cancer is present, excess supplemental folic acid might accelerate the growth rate. That point is simply not completely acknowledged yet, but why risk walking that fine line. Since you don't know if you have cancer until it gets larger at a later stage, it might be that precaution is the order of the day and safe dietary only lower levels recommended until science finds these answers. ref < the study, and next is the simple explanation of study from WebMD> ref
Quite a few studies are available on lowering Homocysteine using vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid. Some point to slight associations for increasing prostate risk while others reveal no change. Higher blood levels of folates and vitamin B12 have also sometimes been associated with more advanced prostate cancers. ref ref Until these issues are fully settled, the precautionary principle to only use food sources is in play and especially restrict use of supplements and never consume excess amounts. ref
Copy of study linked above: "Among the 643 men who were randomly assigned to placebo or supplementation with folic acid, the estimated probability of being diagnosed with prostate cancer over a 10-year period was 9.7% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 6.5% to 14.5%) in the folic acid group and 3.3% (95% CI = 1.7% to 6.4%) in the placebo group..."
- Selenium and Vitamin E on Prostate Health (SELECT Study)
The Select Study looked at Vitamin E and Selenium for their effects on prostate health. The assumption was that earlier research had revealed a positive association of these nutrients on prostate which this study was to verify. But, this 12 year study was halted at the midpoint analysis when no positive influences were found and a slight negative one was discovered for vitamin E on prostate cancer and selenium on diabetes. ref Read more here.
ENTER OMEGA 3
UPDATE (Aug 2013): A new analysis using data from the SELECT study which tested Vitamin E and Selenium on Prostate health, has found a link between prostate cancer and higher omega 3 blood levels. ref Here is a rationale from a Doctor as to why this new report should be taken with less than a grain of salt. ref Here is another Doctor's report on aspects of this study. ref More research is needed to settle conflicting studies. In the meantime, a logical explanation may be forthcoming. One possibility, greater fish and fish oil consumption must also be accompanied by greater anti-oxidants to prevent the oxidation of the very large and unstable omega 3 fats.
OF INTEREST: Fish oil supplements in order to concentrate and increase dosage, require greater processing and this influences and changes the structure of the omega 3 fats, maybe not the best approach.
Plus, it also has to be pointed out as mentioned by one of the Doctors, not all studies of Japanese Men show reduced prostate cancer. The assumption was that since more fish is consumed, and less PC rates are present, it is the fish that is protective. Here is one town where more PC was found in men who consumed fish 4 or more times per week versus 2 or less. Maybe there is more to this fishy story. Like, are the radiation effects still a genetic factor?
THE DOWNWARD PROSTATE CANCER TREND
It has to be pointed out here that the prostate cancer and mortality rates in the United States began declining around 1992 and have slowly been going down since then. Is it just a coincidence that reports about how bad trans-fat began surfacing at this same time? ref Or did the low fat craze in the 1980's finally impact by lowering dairy fats enough to have a significant influence? article


 ) together with an increase in apoptotic markers. These findings suggest that, by targeting the PI3K-ILK1-Akt pathway, IP6 suppresses cell survival, proliferation, and angiogenesis but induces death in prostate cancer cells, which might have translational potential in preventing and controlling the growth of advanced and aggressive prostate cancer for which conventional chemotherapy is not effective. [Cancer Res 2009;69(24):9465–72]
) together with an increase in apoptotic markers. These findings suggest that, by targeting the PI3K-ILK1-Akt pathway, IP6 suppresses cell survival, proliferation, and angiogenesis but induces death in prostate cancer cells, which might have translational potential in preventing and controlling the growth of advanced and aggressive prostate cancer for which conventional chemotherapy is not effective. [Cancer Res 2009;69(24):9465–72]